Myth 1 Vaccines cause autism
> 100 studies debunk the link bet v & asd (autism spectrum disorders)
WHO, CDC & multiple Institutes of Med concluded – there is NO link bet mmr & asd, thimerosal & asd and few health problems are assoc with v
One study has found that the rates of asd did not differ bet immunized & non-immunized sib groups of children with asd









Myth 2 Vaccines contain more Mercury (thimerosal) now than ever
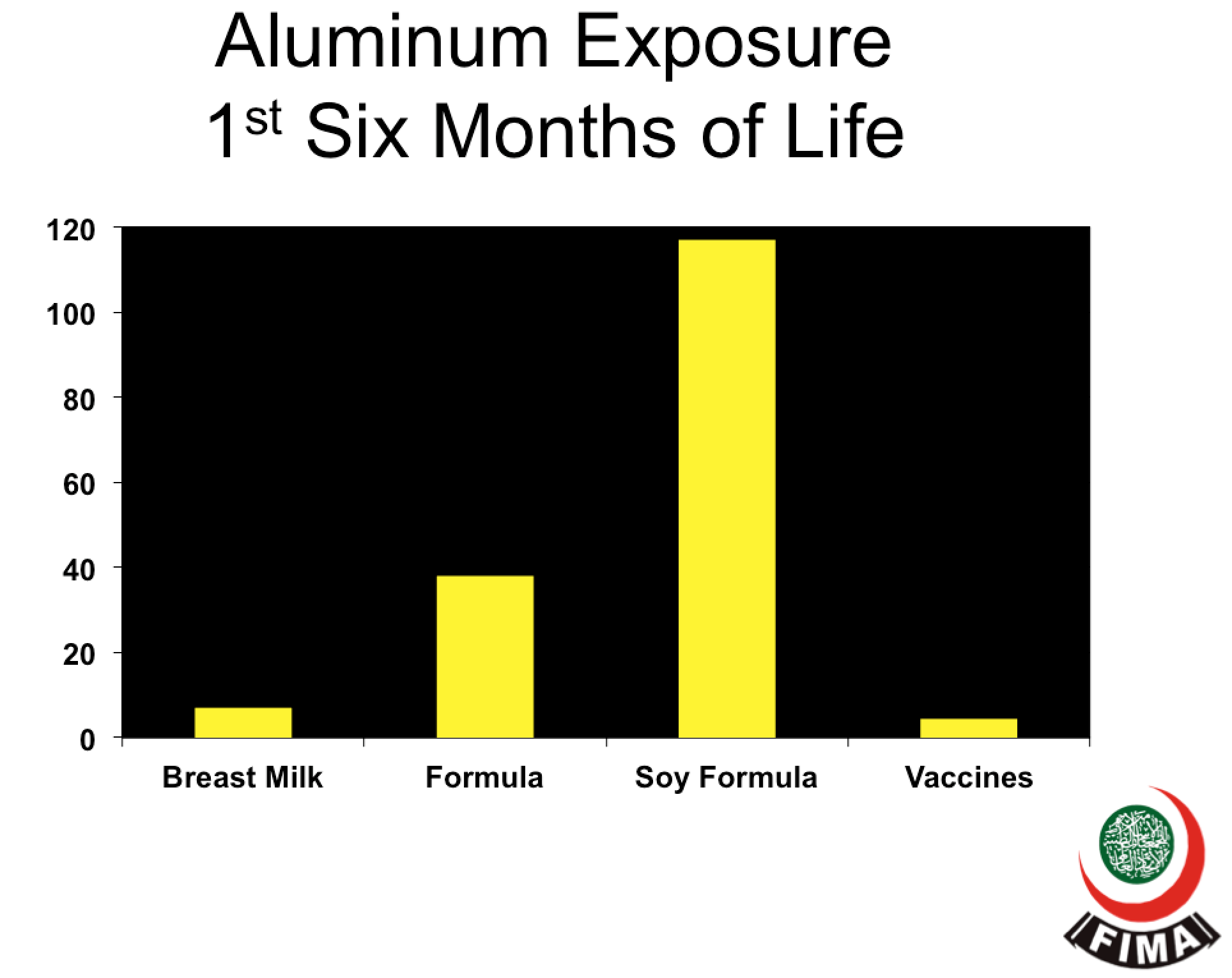
Most vaccines NEVER contained T. Only hep b, dtp & hib & influenza.
With exception of few influenza v; T was removed completely !
Yet asd rates have NOT declined !
T contains ETHYl Mercury which breaks down and is excreted rapidly
Most studies were on METHYl mercury found in fish, low level in water, infant formula & breast MILK which is toxic only in high doses!
Yet harmless in minute quantities
A breastfed baby will ingest > 2X Mercury that from V and 15X Mercury found in influenza V
T used in multi dose v vials to prevent bacterial contamination!
Most of us in private practice do single dose vials ie. no T required
Myth 3: Vaccines are made with aborted fetal tissue
• Varicella, rubella, hepatitis A, shingles and rabies vaccine are made in fetal embryo fibroblast cells.
• First obtained from elective termination of two pregnancies in the early 1960s.
• They were NOT aborted for vaccine research.
• These cells continue to grow in the laboratory
• No further sources of fetal cells are needed.
• No aborted fetal tissue is in the vaccine itself.
Why Human Fetal Cells
• Viruses grow better in cells from humans than animals.
• Cells die after about 50 divisions.
• Fetal cells can go through many more divisions before dying.
• Unequivocal fatwas related to permissible use of cells or organs from:-
a. aborted fetuses (Islamic Org of Medical Sciences IOMS 1989, pg 335)
b. surplus embryos in IVF (IOMS 1987 pg 337)
c. anencephalic baby (IOMS 1989, pg 340)
Myth 4: Better Hygiene & Sanitation caused decreased Infections, not Vaccines
•Smallpox, diphtheria, polio, measles, etc. began to be eradicated at different times !
•If hygiene and better nutrition were the reasons, wouldn’t they all have been eradicated at the same time?
•And why didn’t other diseases, like rotavirus and chicken pox, decrease until so much later, when their vaccines were introduced?
•1963 – 400K measles cases. Measles vaccine introduced and 1970 only 25K cases
Myth 5: Too many too soon – overloading the immune system
•The infant’s immune system is more robust that you might think.
•Babies are exposed to countless germs every day and vaccines are simply negligible!
•If all schedule vaccines were given to infants at one time, only 0.1% of the immune system would be used up.
•The immune system would not be overwhelmed since the cells are constantly replenished.
•With today’s vaccines less antigen are used than in the past.
Myth 6: The HPV vaccine just encourages kids to have sex
•The study “Risk Perceptions and Subsequent Sexual Behaviors After HPV Vaccination in Adolescents” concluded that “risk perceptions after HPV vaccination were not associated with riskier sexual behaviors over the subsequent 6 months.” Pediatrics; Feb 2, 201
•Previous studies showed that “vaccinated, compared with unvaccinated, adolescents were not more likely to initiate sex or participate in risky sexual behaviors after vaccination”
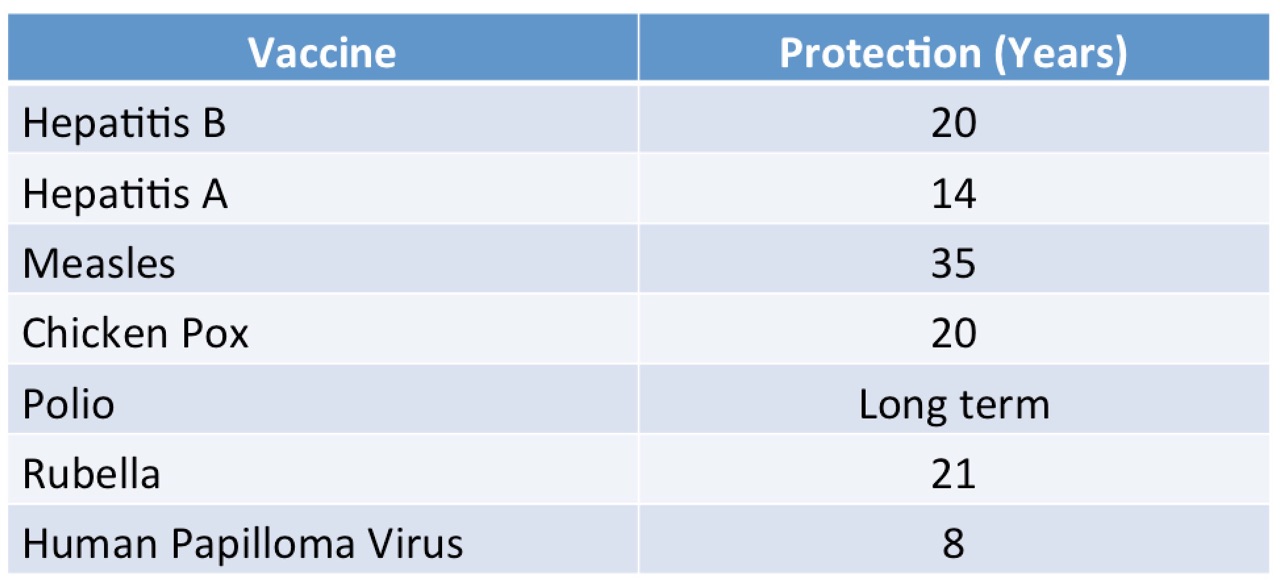
Myth 7: Vaccines don’t stay in your system for a lifetime
Vaccines do provide long-lasting protection, and as studies continue, we will likely find that they provide life-long protection, especially live vaccines.
Myth 8: No one else is at risk if I don’t vaccinate my kids
Unvaccinated kids and adults pose a risk to others, especially those who are too young to be vaccinated and those with immune system problems (eg., immunodeficiencies, cancers etc) who can’t be vaccinated.
Unvaccinated children and adults are responsible for starting most of the outbreaks that we continue to see today.
Almost all of the people who develop measles during outbreaks are unvaccinated or incompletely vaccinated.
Measles outbreak Europe in 2011: 30,000 people cases, causing 8 deaths, 27 cases of measles encephalitis, and 1,482 cases of pneumonia. 82% were unvaccinated & 13% incompletely vaccinated.
Australia 2014: 227 cases – most were unvaccinated.
United States 2015: 170 cases in 17 states and rising. Most were unvaccinated.
2 to 5% do not respond to their first dose of measles vaccine, which is why a second (booster) dose is recommended. More than 99% develop immunity to measles after two doses of a measles vaccine, like MMR.
Measles is fatal in about 0.2% of cases. It is expensive to contain a measles outbreak.